HOME
/
What Are Heat Shrink Tubes?
What Are Heat Shrink Tubes?
What is a heat shrink tube?
Heat shrink tubes are a type of extruded plastic tubing that, when exposed to heat, shrinks in diameter but remains the same in length. This property allows them to form a tight, protective covering over cables, wires, and other objects. They are commonly made from materials such as polyolefin, PVC, and PTFE, which provide durability and flexibility.
Heat shrink tubes play a crucial role in various industries due to their ability to provide insulation, protection, and organization for electrical and mechanical components. In the electrical industry, they are used to insulate wires, provide strain relief, and protect against environmental factors such as moisture and chemicals. In the automotive industry, heat shrink tubes help bundle wires and protect them from abrasion and extreme temperatures. Additionally, they are used in medical devices, aerospace, and consumer electronics, making them an essential component in ensuring the reliability and longevity of a wide range of products.
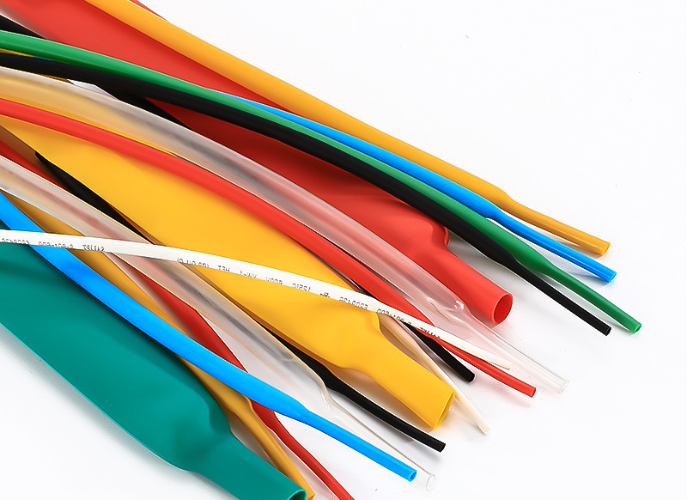

Types of heat shrink tubes
1. Standard Heat Shrink Tubes
Standard heat shrink tubes are the most common type used for general-purpose applications. They are typically made from polyolefin and provide good insulation and protection for wires and cables. These tubes shrink uniformly when heated and are available in various shrink ratios, colors, and sizes to suit different needs.
2. Dual-Wall Heat Shrink Tubes
Dual-wall heat shrink tubes feature an additional layer of adhesive lining on the inside. When heated, the outer layer shrinks, and the inner adhesive melts and flows, creating a moisture-resistant seal. This provides extra protection against environmental factors such as water, dust, and chemicals, making them ideal for use in harsh conditions.
3. Adhesive-Lined Heat Shrink Tubes
Similar to dual-wall tubes, adhesive-lined heat shrink tubes have an inner layer of adhesive. The difference lies in the type of adhesive and its application. These tubes are designed to bond with the surfaces they cover, providing a strong, permanent seal. They are used in situations where a high level of protection and durability is required, such as in automotive and marine environments.
4. Special-Purpose Heat Shrink Tubes
Special-purpose heat shrink tubes are designed for specific applications and environments. Examples include:
* Flame-Retardant Heat Shrink Tubes: These tubes are made from materials that resist burning, providing added safety in fire-prone areas.
* High-Temperature Heat Shrink Tubes: These tubes are capable of withstanding extreme temperatures, making them suitable for applications involving high heat.
* Chemical-Resistant Heat Shrink Tubes: Designed to withstand exposure to harsh chemicals and solvents, these tubes are used in industrial and laboratory settings.
* Mil-Spec Heat Shrink Tubes: These tubes meet military specifications for performance and reliability, used in defense and aerospace applications.
* Each type of heat shrink tube offers unique properties and benefits, allowing for tailored solutions to meet the specific needs of various industries and applications.

How heat shrink tubes work
Heat shrink tubes work through a simple yet effective process involving heat application. The tubes are made from polymer materials that have been stretched during manufacturing. When heat is applied, usually with a heat gun or other heat source, the polymer molecules return to their original, unstretched state, causing the tube to shrink in diameter. This process tightly conforms the tube around the object it covers, creating a secure, protective layer.
The steps involved are as follows:
* Selection: Choose the appropriate size and type of heat shrink tube based on the application.
* Placement: Slide the tube over the object (e.g., wire, cable) that needs to be covered.
* Heating: Apply heat evenly using a heat gun or other heat source until the tube shrinks and fits snugly around the object.
* Cooling: Allow the tube to cool and solidify, ensuring a tight fit and robust insulation.
Shrink Ratios and Their Significance
Shrink ratios are a critical aspect of heat shrink tubes, indicating how much a tube will shrink when heat is applied. The shrink ratio is typically expressed as a ratio, such as 2:1, 3:1, or 4:1.
* 2:1 Shrink Ratio: The tube will shrink to half its original diameter. For example, a tube with a 1-inch diameter will shrink to 0.5 inches.
* 3:1 Shrink Ratio: The tube will shrink to one-third of its original diameter. For instance, a tube with a 3-inch diameter will shrink to 1 inch.
* 4:1 Shrink Ratio: The tube will shrink to one-quarter of its original diameter. For example, a tube with a 4-inch diameter will shrink to 1 inch.
Significance of Shrink Ratios
* Versatility: Higher shrink ratios offer more flexibility in fitting the tube over irregularly shaped or large objects and then shrinking down to a tight fit.
* Compatibility: Choosing the correct shrink ratio ensures compatibility with various sizes and shapes of wires, cables, and connectors, providing a secure and reliable fit.
* Efficiency: Proper shrink ratios help achieve the desired level of insulation and protection with minimal waste of material, ensuring efficient use of heat shrink tubing.

Applications of heat shrink tubes
1. Electrical Insulation
Heat shrink tubes are widely used to insulate electrical wires and components, providing a protective barrier against electrical currents. This prevents short circuits, enhances safety, and ensures the reliability of electrical connections. They are especially useful in areas where exposed wires could pose a risk of electrical shock or fire.
2. Strain Relief
By securely wrapping around connectors and cables, heat shrink tubes provide strain relief, reducing the stress and strain on electrical connections. This helps to prevent damage to the wires and connectors, extending the lifespan of the components and maintaining the integrity of electrical systems.
3. Environmental Protection
Heat shrink tubes offer excellent protection against environmental factors such as moisture, dust, chemicals, and abrasion. When sealed, they create a watertight barrier that protects the enclosed components from corrosion and damage caused by harsh environmental conditions. This makes them ideal for outdoor and industrial applications.
4. Cable Bundling
Heat shrink tubes are used to bundle multiple cables together, keeping them organized and reducing clutter. This not only improves the appearance of the wiring but also makes it easier to manage and maintain. Bundling cables with heat shrink tubes can also help to prevent tangling and accidental disconnections.
5. Repairs and Maintenance
Heat shrink tubes are valuable tools for repairing damaged insulation on wires and cables. They can be used to cover and reinforce areas where the insulation has worn away or been damaged, restoring the protective barrier and preventing further deterioration. This is a cost-effective solution for extending the life of electrical components.
6. Other Specialized Uses
* Medical: In the medical field, heat shrink tubes are used to insulate and protect delicate instruments and devices, ensuring their functionality and sterility.
* Automotive: In automotive applications, heat shrink tubes protect wiring harnesses from heat, abrasion, and exposure to chemicals and oils, ensuring the reliability and safety of the vehicle’s electrical system.
* Aerospace: Heat shrink tubes meet stringent specifications for performance and reliability in aerospace applications, protecting wiring and components in high-stress and high-temperature environments.
* Consumer Electronics: They are used in the assembly and repair of consumer electronics, providing insulation and protection for internal wiring and components.
Heat shrink tubes are versatile and essential tools across various industries, offering protection, organization, and durability to a wide range of applications.

Installation Process
1. Preparation Steps
Select the Right Tube: Choose a heat shrink tube with the appropriate size and shrink ratio for your application. The tube should be slightly larger than the object it will cover before shrinking.
Measure and Cut: Measure the length needed to cover the object and cut the tube accordingly. Ensure that the cut is clean and straight to achieve an even shrink.
Clean the Surface: Clean the surface of the wire, cable, or component to remove any dirt, grease, or moisture. A clean surface ensures better adhesion and a more secure fit.
2. Tools Required
Heat Gun: The most common tool used to apply heat evenly and control the shrinking process.
Lighter or Matches: Can be used for small or quick jobs, but they provide less control and even heat distribution.
Scissors or Utility Knife: For cutting the heat shrink tube to the desired length.
Wire Strippers and Crimpers: If working with electrical wires, these tools may be necessary for preparing the wires before applying the heat shrink tube.
3. Step-by-Step Installation Guide
Step 1: Prepare the Object: If working with electrical wires, strip the insulation from the ends and make the necessary connections (e.g., crimping or soldering).
Step 2: Slide the Tube: Slide the heat shrink tube over the object before making the final connection if possible. Ensure the tube is positioned correctly.
Step 3: Apply Heat Evenly: Using a heat gun, apply heat evenly around the heat shrink tube. Move the heat gun back and forth to avoid overheating any one area. If using a lighter, be very careful to apply heat evenly and avoid direct flames on the tube for too long.
Step 4: Observe the Shrinkage: Watch as the tube shrinks uniformly around the object. The tube should conform tightly and smoothly to the shape of the object.
Step 5: Complete the Process: Continue applying heat until the tube has fully shrunk and there are no gaps or wrinkles. For adhesive-lined tubes, ensure the adhesive flows and forms a seal.
Step 6: Allow to Cool: Let the tube cool and solidify. The cooling process ensures that the tube retains its shape and provides a secure fit.

Advantages
1. Durability and Reliability
Heat shrink tubes are designed to be highly durable and reliable. They provide long-lasting protection for wires and components, resisting wear and tear from environmental factors such as moisture, chemicals, and abrasion. This durability ensures that electrical connections remain intact and secure over time, reducing the need for frequent maintenance or replacement.
2. Versatility in Applications
Heat shrink tubes are versatile and can be used in a wide range of applications across various industries. They are available in different sizes, colors, and shrink ratios, making them suitable for everything from small electronic components to large industrial cables. Their ability to provide insulation, strain relief, and protection makes them valuable in electrical, automotive, aerospace, medical, and consumer electronics applications, among others.
3. Ease of Use
Installing heat shrink tubes is straightforward and requires minimal tools. The process involves simply sliding the tube over the object and applying heat, making it accessible even for those with limited technical skills. This ease of use allows for quick repairs and installations, saving time and effort compared to other methods of insulation and protection.
4. Protection and Safety Benefits
Heat shrink tubes offer significant protection and safety benefits. They provide effective insulation for electrical wires, reducing the risk of short circuits and electrical shocks. The tight, conforming fit created by the shrinking process also provides strain relief, preventing mechanical damage to wires and connectors. Additionally, special-purpose heat shrink tubes, such as flame-retardant and high-temperature varieties, offer enhanced safety features for specific applications, ensuring compliance with safety standards and regulations.

Considerations and Limitations
1. Proper Selection Based on Application
Material: Choose the appropriate material for your application. Polyolefin is common for general use, while PTFE or PVC may be needed for specific environments.
Shrink Ratio: Select the right shrink ratio to ensure a snug fit. For irregularly shaped objects, higher shrink ratios like 3:1 or 4:1 may be more suitable.
Size: Ensure the tube’s diameter before shrinking is slightly larger than the object it will cover. After shrinking, it should fit tightly without gaps.
Special Requirements: Consider any special needs such as flame retardancy, UV resistance, or flexibility for your specific application.
2. Potential Limitations
Temperature Range: Heat shrink tubes have specific operating temperature ranges. Exceeding these limits can cause degradation or failure. For high-temperature environments, use materials designed to withstand higher heat.
Chemical Resistance: Some materials may not resist certain chemicals or solvents. Ensure the selected tube material is compatible with the chemicals it may be exposed to.
Mechanical Strength: While heat shrink tubes provide good protection, they may not offer sufficient mechanical strength in all scenarios. For heavy-duty applications, additional protection might be necessary.
Environmental Factors: Consider factors like UV exposure, moisture, and abrasion. Select tubes designed to withstand these conditions if applicable.
3. Common Mistakes to Avoid
Incorrect Sizing: Using a tube that is too large or too small can result in improper insulation and protection. Always measure and select the correct size.
Uneven Heating: Applying heat unevenly can cause incomplete shrinking or damage to the tube. Use a heat gun for controlled and uniform heating.
Overheating: Excessive heat can damage the tube or the underlying components. Use moderate heat and avoid direct flames unless necessary for small jobs.
Ignoring Surface Preparation: Failing to clean the surface before applying the tube can result in poor adhesion and protection. Always clean and dry the surface thoroughly.
Inadequate Overlap: Ensure the tube extends beyond the area it covers to provide complete protection and a secure fit.
Conclusion
Heat shrink tubes are an essential component in a variety of industries, offering reliable insulation, protection, and organization for electrical and mechanical systems. Their versatility allows them to be used in numerous applications, from electrical insulation and strain relief to environmental protection and cable bundling.
Understanding the different types of heat shrink tubes, such as standard, dual-wall, adhesive-lined, and special-purpose, helps in selecting the right tube for specific needs. The installation process is straightforward, requiring only a few tools and basic steps to achieve a secure fit.
The advantages of heat shrink tubes, including durability, reliability, ease of use, and significant protection and safety benefits, make them indispensable for professionals and hobbyists alike. However, it is crucial to consider potential limitations such as temperature range and chemical resistance, and to avoid common mistakes like incorrect sizing and uneven heating.
By carefully selecting and properly installing heat shrink tubes, users can enhance the performance and longevity of their electrical and mechanical systems. This ensures a safer, more organized, and efficient operation in various applications. As technology advances, the continued development and innovation in heat shrink materials and designs will further expand their utility and effectiveness.